Choosing transistors for high-power digital switching
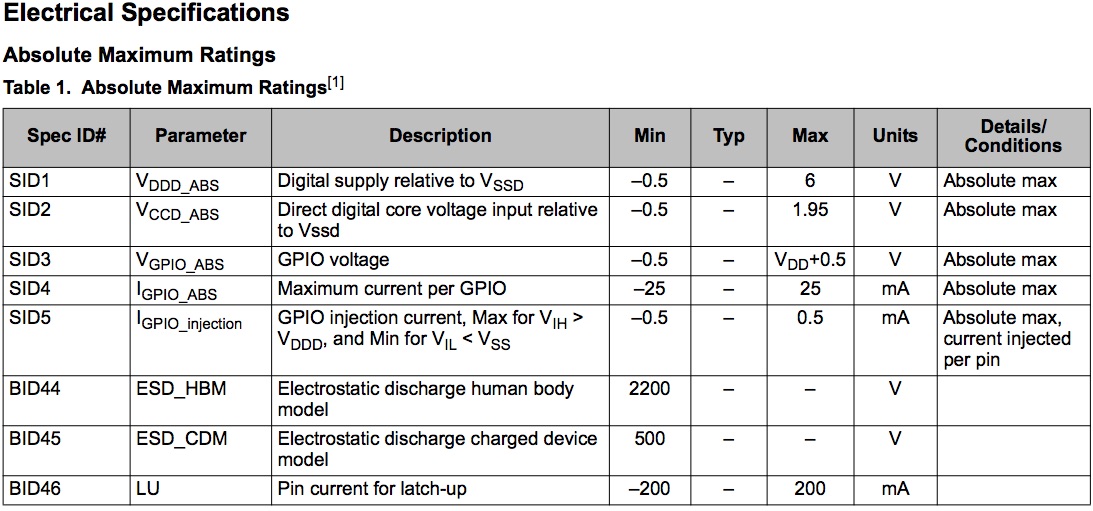
Microcontrollers make wonderful “brains” for embedded systems, but are severely limited in the amount of current they can supply to an external device. In order to determine the amount of current a microcontroller can supply (or sink) with an output pin, open the data sheet and look for the section describing “Absolute Maximum Ratings”. There, there should be a specification described as the maximum current for a single GPIO pin (see example, Figure 1).
Figure 1: Example Absolute Maximum Ratings table from a PSoC 4200 datasheet |
In the example above, the maximum current that can be sourced/sunk with an I/O pin is 25 mA. Therefore, if you are trying to control an external device that draws 100 mA, the microcontroller can not supply the full amount of current. Or, if your motor requires 12V and the microcontroller only supplies 5V, there is also a mismatch.
Solution: Add a transistor to interface between the low voltage/low current provided by the microcontroller to the high voltage/high current required by the actuator! Dr. Jordan has put together a detailed presentation on choosing an appropriate transistor for use in high-power digital switching.